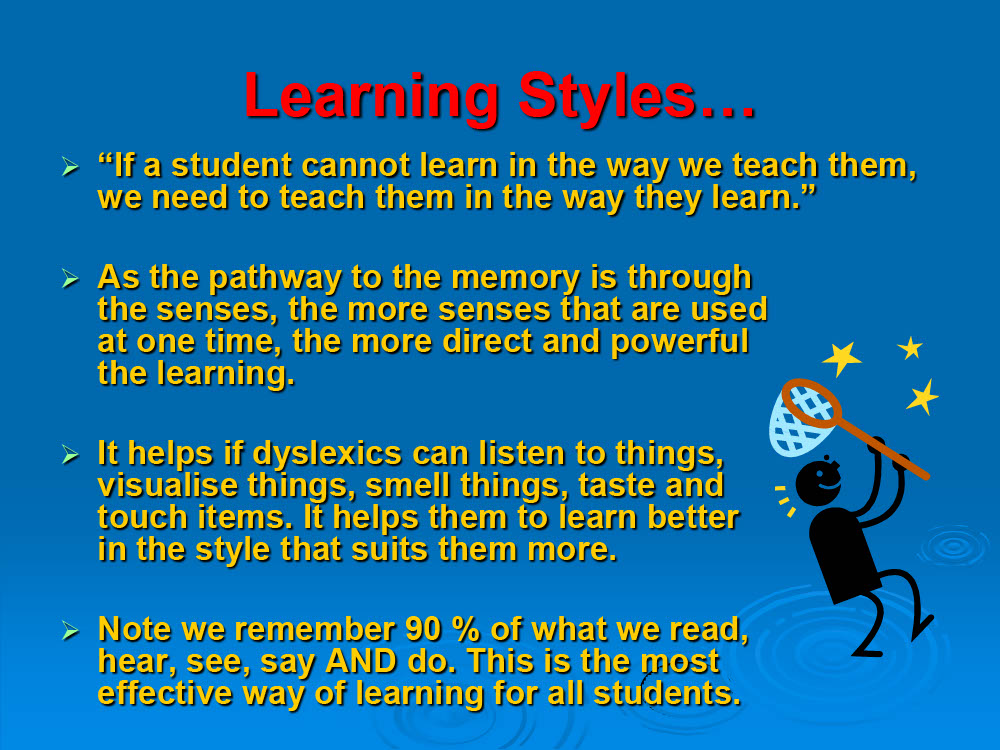
Definitions of Dyslexia
Rose Definition of Dyslexia (“Identifying and Teaching Children and Young People with Dyslexia and Literacy Difficulties” An independent report from Sir Jim Rose to the Secretary of State for Children, Schools and Families, June 2009)
Dyslexia is a learning difficulty that primarily affects the skills involved in accurate and fluent word reading and spelling. Characteristic features of dyslexia are difficulties in phonological awareness, verbal memory and verbal processing speed. Dyslexia occurs across the range of intellectual abilities. It is best thought of as a continuum, not a distinct category, and there are no clear cut-off points. Co-occurring difficulties may be seen in aspects of language, motor co-ordination, mental calculation, concentration and personal organisation, but these are not, by themselves, markers of dyslexia.
A good indication of the severity and persistence of dyslexic difficulties can be gained by examining how the individual responds or has responded to well-founded intervention.
The British Dyslexia Association (BDA) has adopted the Rose (2009) definition (above).
In addition to these characteristics:
The BDA acknowledges the visual and auditory processing disorders that some individuals with dyslexia experience and points out that dyslexic readers can show a combination of abilities and difficulties that affect the learning process. Some also have strengths in other areas, such as design, problem solving, creative skills, interactive skills and oral skills.
(BDA 2010)
Feel free to check out these two slideshows that go in-depth into dyslexia: